AI - Retrieval Augmented Generation
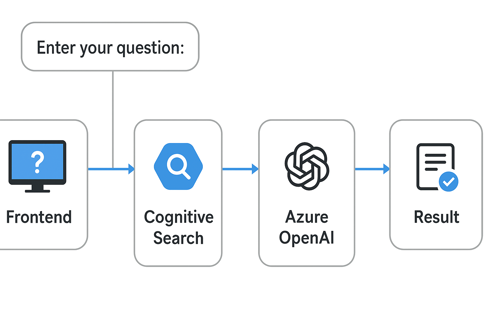
This approach gives you the best of both worlds:
-
Cognitive Search = retrieves relevant orders/comments from your database index.
-
Azure OpenAI = interprets the user’s question, analyses retrieved documents, and generates a summarised or aggregated answer.
Flow:
-
User enters a natural language question in your frontend.
-
Cognitive Search retrieves the most relevant Orders.Comments.
-
The retrieved results are passed as context to Azure OpenAI (GPT model).
-
OpenAI generates a concise, human-friendly response (summary, count, or explanation).
Example C# Implementation (RAG Pattern):
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Azure;
using Azure.Search.Documents;
using Azure.Search.Documents.Models;
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// ====== Cognitive Search Setup ======
string searchEndpoint = "https://<your-search-service>.search.windows.net";
string searchApiKey = "<your-search-key>";
string indexName = "orders";
var searchClient = new SearchClient(
new Uri(searchEndpoint),
indexName,
new AzureKeyCredential(searchApiKey));
// ====== OpenAI Setup ======
string openaiEndpoint = "https://<your-openai-resource>.openai.azure.com/";
string openaiKey = "<your-openai-key>";
string deploymentName = "<your-gpt-deployment>"; // e.g. "gpt-35-turbo"
var openaiClient = new OpenAIClient(new Uri(openaiEndpoint), new AzureKeyCredential(openaiKey));
// ====== User Input ======
Console.WriteLine("Enter your question:");
string userInput = Console.ReadLine();
// Step 1: Retrieve relevant documents from Cognitive Search
var searchOptions = new SearchOptions()
{
Size = 5,
QueryType = SearchQueryType.Semantic,
QueryLanguage = "en-us"
};
searchOptions.Select.Add("orderId");
searchOptions.Select.Add("comments");
var searchResults = searchClient.Search<SearchDocument>(userInput, searchOptions);
string retrievedText = string.Join("\n",
searchResults.GetResults()
.Select(r => $"Order {r.Document["orderId"]}: {r.Document["comments"]}"));
// Step 2: Send retrieved docs + user query to Azure OpenAI
string systemPrompt = @"
You are a helpful assistant that analyzes order comments.
Use the provided context to answer the user’s question.
If context is insufficient, say you don’t know.
"; var chatOptions = new ChatCompletionsOptions()
{
Temperature = 0.2f,
MaxTokens = 800
};
chatOptions.Messages.Add(new ChatMessage(ChatRole.System, systemPrompt));
chatOptions.Messages.Add(new ChatMessage(ChatRole.User,
$"Question: {userInput}\n\nContext:\n{retrievedText}"));
var response = await openaiClient.GetChatCompletionsAsync(deploymentName, chatOptions);
// Step 3: Output final answer
Console.WriteLine("\nAnswer:");
Console.WriteLine(response.Value.Choices[0].Message.Content);
}
}
Example Use Cases
User query:
“Show me all the orders where delivery is delayed due to an invalid address.”
-
Cognitive Search: retrieves 5 orders with matching comments.
-
OpenAI: formats a human-readable list (Order IDs + short summary).
User query:
“How many customers mentioned weather problems?”
-
Cognitive Search: retrieves comments mentioning "weather".
-
OpenAI: counts them and responds like: “3 orders reported weather-related delays.”
Benefits of RAG
-
Keeps OpenAI responses grounded in your data (avoids hallucinations).
-
Works on large databases by only sending relevant slices to OpenAI.
-
Flexible: can answer fact-based queries (counts, filters) and generate natural summaries.
No files yet, migration hasn't completed yet!